Power Blackout Committee Report:Recommendations run counter to President’s policy
Posted on September 2nd, 2020
By Dr. Janaka Ratnasiri Courtesy The Island
The Minister of Power, four days after assuming duties, had to face an island-wide power blackout which commenced around 12.30 pm on the 17th August and lasted up to 7-8 hours. The following day, he appointed a committee, comprising Ministry officials and power experts, to investigate the matter and submit a report within a week.
COMMITTEE APPOINTED BY THE MINISTER
The Committee comprised two administrative officers, including an Additional Secretary to the Ministry of Power, serving as the Chairman, a Retired Professor of Mechanical Engineering, an Engineer who is a Chairman of a Corporation, two Senior Lecturers in Electrical Engineering, one senior official from the Ceylon Electricity Board (CEB) and one senior official from the Ministry of Power responsible for Renewable Energy Development. The Director General of the Public Utilities Commission of Sri Lanka (PUCSL) was also nominated but did not serve as there was a separate investigation being undertaken by the PUCSL. With two members from the Ministry, including one in the Chair, and another from CEB, the Committee cannot be considered as independent.
The Committee had met on the 18th and submitted an interim Report, to the Minister, on the 24th, which was also tabled at the Cabinet meeting held on the 26th. The Report was also made available at a press briefing held by the Ministry and the contents herein are taken from this Report. According to the Report, the Committee had visited the Kerawalapitiya Grid Substation (GSS) where the initial fault occurred claimed to be due to a human error, Lakvijaya Power Station (LVPS) at Norochcholai, Protection Branch of the CEB and the System Control Center of the CEB at Pelawatta, and had interviewed the staff on duty at these stations with a view to elicit information on the following.
The key reasons for the nationwide power interruption on the 17th August 2020 at 12:30 pm onwards.
Whether the CEB has taken precautionary actions and measures to prevent recurrence of interruptions that had been encountered in the recent past for which recommendations have been extended by similar committees that could have influenced the present incident.
Recommendations for remedial measures that need to be taken by the CEB to prevent recurrence of the same and similar incident.
Whether the CEB has taken the best professional practicing measures in handling the incident and the conditions that led to it employing proper planning, operational and administrative elements and had any constraint encountered CEB’s intended professional actions.
Whether the CEB had encountered similar incidents in the past and how the situation had been then handled.
Whether the CEB could have handled the situation judiciously to minimize the implication and how this could be avoided in the future.
PRELIMINARY FINDINGS OF THE REPORT
The Committee, in its Interim Report ,has given a set of preliminary findings, among which are the following:
Routine maintenance work on the 220 kV isolators of the Bus Coupler Bay had been carried out on the day of the incident by the Electrical Superintendent-In-Charge at Kerawalapitiya GSS, who apparently has been attending routine maintenance work at the Kerawalapitiya GSS for the past five years. The power in the Bus Bar 01 had been turned OFF for the maintenance, while the power of the Bus Bar 02 was ON. The Earth Switch 01 at Bus Bar 01 side had been OFF while the Earth Switch 02 at Bus Bar 02 side had been ON as shown in Fig. 1.2(a) at the time of incident.
Under normal operations the Earth Switch and the relevant isolator are interlocked, so that the isolator cannot be turned ON while the Earth Switch is turned ON. However, during maintenance, this interlock had been bypassed, so that isolator can be turned ON even with the Earth Switch is turned ON. At the end of the maintenance work of the 220 kV Bus Coupler Bay, while the interlock is bypassed, the Isolator on the Bus Bar 02 side had been turned ON as shown in Fig. 1.2(b), creating a 3 Phase to Ground fault.
The key reason for the nationwide power interruption on the 17th August 2020 is due to the 3 Phase to Ground busbar fault due to incorrect operation of the Bus Bar 2 Isolator of the Bus Coupler Bay by the Electrical Superintendent -in-Charge at the Kerawalapitiya Grid Substation busbar at 12:30 Hrs.
Kerawalapitiya Grid substation tripping was due to not following the correct maintenance procedure by the relevant officials including the Electrical Superintendent. The Committee also observed that there was no written maintenance protocol for this maintenance job in-line with the current best practiced maintenance protocols.
The Committee is of the view that due to the Kerawalapitiya Grid substation tripping, the system frequency has increased beyond the current setting of the rate of frequency tripping relay of the Lak Vijaya Power Station (LVPS). As a result, the generator-transformer circuits breakers of all three units of the LVPS which made LVPS unavailable to the grid, subsequently the system failed in cascade.
CEB’s recent failure to avoid a country-wide blackout and the longer duration taken to restore power to Colombo City in particular, indicates significant lapses in implementation of critical measures outlined in the previous Expert Committee Reports.
AUTHOR’S COMMENTS ON THIS PROCEDURE
The cardinal mistake done by the Electrical Superintendent (ES) during the maintenance work was that he had disabled the interlocking system which prevents switching on the 220 kV line to the GSS while it is earthed, which is a protective mechanism incorporated into the system to prevent blunders by maintenance staff as happened. It is certainly not an Ath Wereddak” as claimed by a senior official of the CEB. As a result, the ES was able to connect the high voltage line to the substation already earthed which created the havoc.
The question which arises is what was the necessity to disable the interlocking system to carry out the routine maintenance? The Report does not seem to have queried the ES on this. If the ES has done such an irresponsible act, deliberately, in any other organization, he would have been interdicted forthwith or at least sent on compulsory leave. But, the CEB Management thought otherwise, possibly for fear of trade union reaction.
The tripping of the 220 kV line at Kerawalapitiya apparently has caused a sudden increase in the system frequency at LVPS, resulting in the three generating units there to trip. A sudden increase in the frequency means that the speed of the generator rotors has increased suddenly. Isn’t there a mechanical device called a governor in the generator which helps in maintaining the rotor speed at a constant value? Is it a characteristic of a coal power plant to allow its rotor speed to vary suddenly in response to a disruption in the line? Was it that this governor did not function properly when this incident took place?
The CEB management should be faulted for not making available to the maintenance personnel proper maintenance manuals. It was alleged that even for the Norochcholai coal plant, the manufacturer never made available to CEB the operation manuals in English. That may be the reason for having Chinese technicians to attend to O&M functions even today. It seems that during the last 6-7 years since commissioning the plant, CEB personnel have not been able to learn the O&M functions from the
Chinese technicians. Though, the CEB staff at Norochcholai are unable to handle the O&M functions of the coal power plant by themselves, Sri Lankan personnel are managing three combined cycle power plants, two at Kelanitissa and one at Kerawalapitiya. This is one more reason why Sri Lanka should not build any more coal power plants.
RECOMMENDATIONS OF THE REPORT
Among the recommendations made by the Committee are the following among others:
The committee strongly recommends a standard compliant, systematic, foolproof, safe procedures and maintenance protocols to be instated in the CEB during operation and maintenance (O&M). The implementation of these procedures will have to be continuously monitored and supervised by adequately qualified, professionally trained, knowledgeable, experienced and skilled personnel. The committee would like to propose a performance evaluating annual appraisal system which will help to improve the above attributes of the CEB staff.
The committee understands that there is no Operations & Maintenance related risk management mechanism in place. Therefore, it is recommended to establish a risk management mechanism in order to determine the proper mix of preventive measures, mitigation levels, shift or retention of risks and consequent level of robustness of Operations & Maintenance protocols that would indicate the positive impact on the overall system
The committee strongly recommends to implement the 2018-2037 CEB Long Term Generation Expansion Plan, as given in the plan, which clearly specifies the correct blend of technologies for the future requirements of the Sri Lankan power system to improve the system stability and reliability.
The committee recommends to review the existing protection strategy for frequency instability.
2018-2037 LONG-TERM GENERATION
EXPANSION PLAN
The first two recommendations are in order. One would expect that an organization like the CEB has already following proper standard procedures for O&M. But if they are lacking, priority needs to be given for the training of staff adequately. It has been alleged in the media that all foreign training programmes are given to engineering staff while the middle level technical staff who actually carry out the O&M work are given only local training. Perhaps, there is a case here and if it is true, it should be rectified.
Since the Committee has made a strong recommendation that the CEB’s 2018-2037 Long-Term Generation Plan be implemented, it is necessary to examine what this plan is. The CEB prepares biennially a long-term generation expansion (LTGE) plan outlining the least cost options of generation plants that need to be added to the system annually for the next 20 years to meet the forecasted demand. The latest plan is in respect of the period 2020 – 2039 but it is still in the draft form yet to be approved by the PUCSL as required by Sri Lanka Electricity Act No. 31 of 2013.
The CEB 2018-2037 LTGE Plan released in June 2018 provided for adding 2,700 MW of coal power capacity between 2023 and 2035 and 1,500 MW of natural gas capacity between 2019 and 2036, along with several gas turbines and diesel power plants as well as a large number of small renewable energy plants comprising mini-hydro, solar, wind and biomass systems, under Base Case scenario. However, the PUCSL did not approve this plan but recommended an alternative plan incorporating natural gas power plants in place of coal power plants included in the CEB Plan.
The CEB refused to accept this recommendation, particularly with objections raised by its Engineers’ Union (EU), and the dispute between the PUCSL and the CEB kept dragging for over a year, and the matter was finally referred to the President who gave a directive to the PUCSL to approve the CEB Plan, fearing disruption to the power supply in the country after the CEB EU threatened to resort to industrial action if their demand for coal power plants is not acceded to. This is something not expected from a body of professionals and unheard in other countries.
Also, the LTGE Plan is highly flawed. It is supposed to determine which power technology will be the cheapest in 20 years hence based on current prices. With the cost of generation depending on plant capital cost and fuel prices both of which could vary widely within a span of 20 years, it is futile to make forecasts now as to which technology is the cheapest in 20 years hence and to adopt it. Although the CEB 2018-2037 Plan has recommended building 2,700 MW of coal power plants on grounds that coal power is the cheapest option, a report by World Bank Group study on Sri Lanka Energy Infrastructure Sector Assessment Programme (InfraSAP) released in February 2019, says in p. 18 that coal ceases to be the least cost source of power generation, as cost of power from LNG and NCRE could potentially be lower than US cents 9 / kWh” which is the estimated coal power price.
It is therefore obvious that the 2018-2037 Plan is not a plan approved after considering engineering and economic aspects properly but approved on political grounds. Hence, the Committee’s strong recommendation to implement such a flawed plan is an attempt to take the power sector development in the country along a wrong path. It is not surprising that the Committee has made such a biased recommendation when two senior officials from the Ministry and one from the CEB are in the Committee. In any case, building more coal power plants is not a solution to a possible blackout in the future. This is the second attempt when the Ministry tried to get building of coal power plants inserted into a policy document on the sly. The first attempt was when the Cabinet took a decision on post-Covid activities to be undertaken urgently in view of the emergency” situation in the country, building a 300 MW coal power plant at Norochcholai was inserted as one activity in the Cabinet decision.
It is also mentioned that the implementation of the CEB 2018-2037 Plan with more coal power plants is recommended to improve the system stability and reliability in the future. The Committee has not justified that the system stability and reliability would be better with coal power plants than with natural gas power plants for the Committee to make such a statement. However, it was shown in this instant that it was the instability of rotor speed of the coal power plants resulting in raising the frequency suddenly that caused the three coal power plants to trip. Hence having more coal power plants will not be of any help to maintain the stability of the system. On the contrary, it will make it worse.
Further, it is noted that with a coal power plant once shut down, it is necessary to wait several days until it cools down before it can be re-started. On the other hand, with a natural gas operated combined cycle power plant, there is no such delay and the plant can be energized within a few hours.
RECOMMENDATION VIOLATING THE PRESIDENT’S POLICY
In the President’s policy document, Vistas of prosperity and splendour”, he says We also anticipate that hydro and renewable energy together would account for 80% of the overall energy mix by 2030”. The State Minister for Renewable Energy said during his assumption of duties that the Ministry’s target is to use renewable energy resources to generate at least 80% of the total generation of electricity by 2030. The Power Minister has also made a statement to that effect in the Parliament. However, it is not possible to achieve this target if the CEB 2028-2037 Plan is implemented.
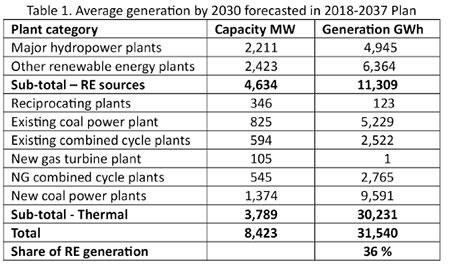
The LTGE Plan has worked out the average generation from each plant type annually and the values obtained for 2030 are given in Table 1, extracted from the data given in Annexes 7.4 of 2018-2037 LTGE Plan. It is to be noted that it is not possible to forecast exact values for generation from each category in the future because it depends on many extraneous factors, such as rainfall, cloud cover, wind regime, fuel prices and demand which are not known accurately in advance. Annex 7.4 gives average values after considering several scenarios.
It is seen that according to the CEB’s LTGE Plan for 2018-37, generation from renewable sources could reach only 36% by 2030, which is far below the 80% target given in President’s VPS Policy Document, assuming what is intended by total energy” appearing in this document is total electricity generation.
Therefore, the Committee’s strong recommendation that the CEB’s 2018-2037 Plan be implemented is a gross violation of the President’s Policy. It is surprising that a learned Committee including several officials in the Ministry, are not aware of the President’s policy. The Power Minster should call for explanations from the Committee Members why they overlooked the President’s Policy when they made their recommendation.